RFID And Its Types
An introduction to RFID, its components and types
Introduction To RFID
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is Automatic Data Collection through Contactless Transfer of information.
It uses radio-frequency waves to transfer data between a reader and a movable item to identify, categorize, track and many more depending upon the application.
RFID Components
There are 2 RFID components:
RFID Tags
RFID Reader
RFID Components
RFID tags and RFID reader

RFID Tags
RFID tags have been classified into following 2 types:
Active Tags
Uses its internal power source to supply energy without the acquiring power from RFID reader to initialize.
Passive Tags
Employs the electromagnetic energy transmitted by RFID reader to initialize its functions.

RFID Readers
RFID readers have been classified into following 2 types:
Fixed Reader
Fixed RFID readers automate data capture at key entry and exit points, such as building entrances or the door to the IT data center, and typically require external antennas to either sides of the portal.
Handheld Reader
Handheld RFID readers allow on-the-spot reading of RFID tags, allowing workers to perform quick and accurate inventories or search for specific items on a warehouse shelf or in a store dressing room.
4 Step Data Transfer
RFID tags data transfer process
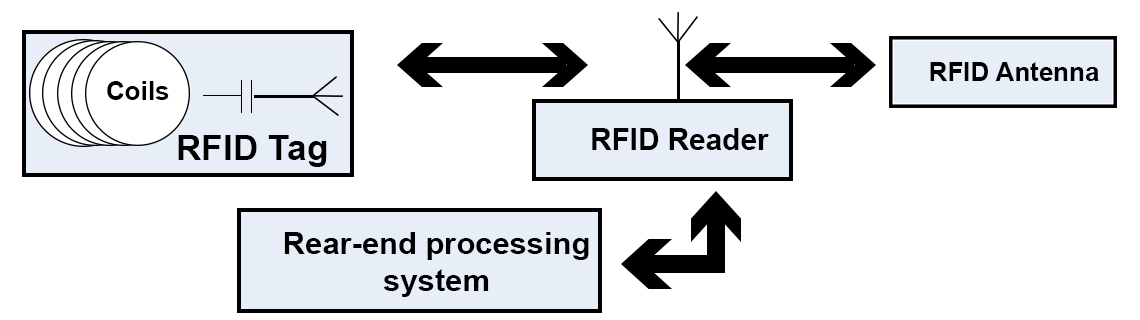
RFID Characterization
RFID characterization
The frequency characteristics also define which applications are best suited for each technology. For example, NFC has become the defacto standard for ticketing and payment because of its short read range and established payment protocols. Alternatively, the long read ranges and low tag costs in the UHF frequency are ideal for inventory, supply chain and asset management visibility.
UHF Basics
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology uses radio waves to exchange identification and tracking data between an RFID reader and an electronic RFID tag that is attached to an object, such as a shipment of products, a forklift in a warehouse or even an employee badge. A microchip in the RFID tag contains the data. In read-only tags, the data can only be captured. In read-write tags, the data can be captured, new data can be appended to the existing data set or new data can completely overwrite the existing information on the tag. The antenna on the RFID reader enables the communication between the tag and reader. The distance that an RFID tag can be read depends on a number of factors, including the environment, as well as the size and type of RFID tag.
Ultra High Frequency (UHF) RFID is especially exciting to the business world because it offers long read ranges with low cost RFID tags, allowing organizations to tag and automatically track large quantities of goods and assets. Typical read ranges for UHF passive tags are 8 to 30 feet (2.4 m to 9.14 m) and beyond.
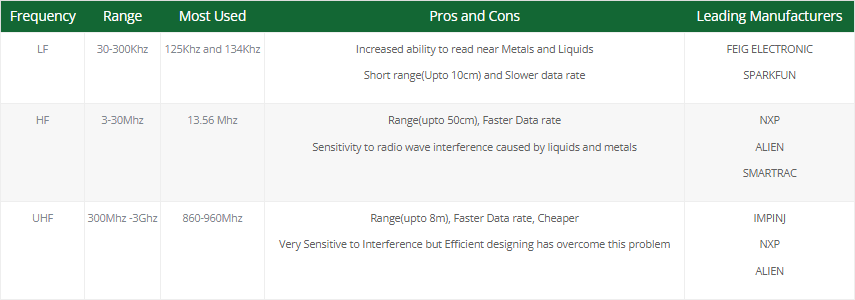
RFID Frequencies
RFID frequencies and ranges
There are three main frequency ranges:
- Low Frequency (LF)
- High Frequency (HF)
- Ultra High Frequency (UHF)